They have typical laboratory findings, including hypokalemia, metabolic alkalosis, hypomagnesemia, and hypocalciuria.
在此篇文章中,我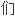
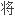
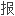 告三个
告三个 例:一是
例:一是
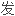
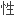 个案,另两位是姐弟。
个案,另两位是姐弟。
声明:以上例句、词性分类均由互联网资源自动生成,部分未经过人工审核,其表达内容亦不代表本软件的观点;若发现问题,欢迎向我们指正。
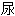
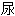
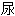
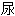
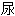
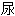
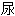
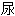
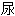
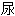
Individuals with hyperaldosteronism typically develop hypertension related symptoms like headaches and facial flushing, as well as hypokalemia related symptoms like constipation, weakness, and potentially changes in their heart rhythm.
醛固酮增多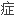 患者通常会出现高血压相关
患者通常会出现高血压相关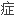 状,如头痛和面部潮红,以及低钾血
状,如头痛和面部潮红,以及低钾血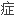 相关
相关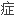 状,如便秘、乏力与对心律的潜在影响。
状,如便秘、乏力与对心律的潜在影响。
All right, as a quick recap, hyperaldosteronism is the chronic, excess secretion of aldosterone from the zona glomerulosa of the adrenal gland, and these high aldosterone levels can lead to hypokalemia, hypernatremia, hypertension, and a metabolic alkalosis.
得!简单回顾 下:醛固酮增多
下:醛固酮增多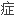

 肾上腺球状带长期分泌过多的醛固酮;这些高醛固酮水平可导致低钾血
肾上腺球状带长期分泌过多的醛固酮;这些高醛固酮水平可导致低钾血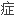 、高钠血
、高钠血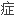 、高血压与代谢性碱中毒。
、高血压与代谢性碱中毒。
As hypokalemia becomes more severe especially in patients with other heart conditions, the inward current may exceed the outward current resulting in early after depolarization and consequently extra heartbeats prolonged repolarization may also promote re-entrant arrhythmias.
随着低钾血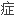 变得更加严重,尤其
变得更加严重,尤其 其他心脏病患者,内向电流可能会超过外向电流,从而导致早期去极化后,因此,额外的心跳延长复极也可能促进折返性心律失常。
其他心脏病患者,内向电流可能会超过外向电流,从而导致早期去极化后,因此,额外的心跳延长复极也可能促进折返性心律失常。
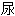
All that being said, in situations where somebody produces too much aldosterone, like primary hyperaldosteronism, then there's more potassium secretion by the principal cells and excreted, and therefore less potassium is retained, leading to hypokalemia.
说了这么多,在某 产生了太多醛固酮的情况下,比如原发性醛固酮增多
产生了太多醛固酮的情况下,比如原发性醛固酮增多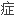 ,更多的钾被主细胞分泌并排泄,这意味着更少的钾被保留,导致了低钾血
,更多的钾被主细胞分泌并排泄,这意味着更少的钾被保留,导致了低钾血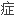 。
。
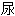
Taken together, a relatively high potassium concentration in the principal cell and a relatively low potassium concentration in the lumen, strengthens the potassium gradient and causes a lot of potassium to get secreted and excreted in the urine - leading to hypokalemia.
总之,主细胞中相对高的钾浓度和管腔中相对低的钾浓度,强化了钾的浓度梯度,造成了许多钾被分泌和排泄入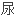 液,导致低钾血
液,导致低钾血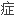 。
。