Most of the main groups of the animal kingdom—arthropods, brachiopods, coelenterates, echinoderms, molluscs and even chordates, the branch from which vertebrates went on to develop—are found in the fossil beds of the Cambrian.
人们在寒武纪群落里发现了动物王国的主要动物集群,包括腕足、腔肠、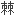
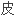 、软体和脊索(脊椎动物进化的分支)。
、软体和脊索(脊椎动物进化的分支)。
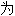 我们今天看到的
我们今天看到的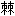
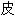 动物铺平了道路。
动物铺平了道路。