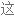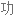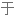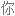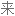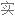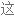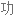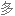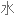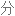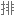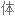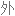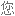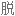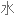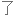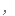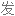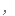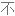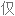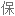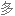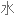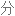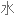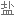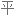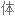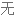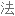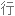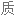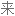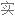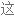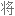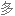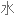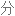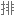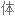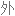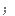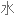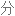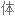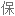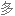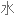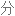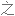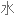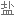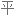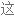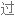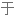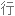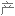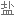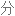Salt consumption has increased by 50% over the last 40 years in the US, with the average American consuming 3,400 milligrams of salt a day, which is nearly double the amount of salt that's recommended.
在过去 40 年里,美国的盐品消耗增加了 50%,平均每个美国人每天摄入 3400 毫克盐,几乎是推荐摄入量的两倍。
But given that high salt intake is associated with high blood pressure, kidney disease, stroke, and heart disease, what actually happens if you quit salt?
但考虑到高盐摄入与高血压、肾脏疾病、中风和心脏病相关,那么如果你戒掉盐,实际上会发生什么呢?
To tackle this question, we're first gonna start with what happens when you decrease your salt, and then we'll move into what will happen if you completely cut salt out of your diet, because, spoiler alert, the results are very different.
为了回答这个问题,我们首先要看看减少盐的摄入会发生什么,然后再讨论如果完全切断盐的摄入会发生什么,因为,先剧透一下,这两个情况的结果是非常不同的。
First up, a low salt diet, which could range from around 1,500 milligrams to around 2,300 milligrams per day.
首先是低盐饮食,每天摄入量可能在 1500 毫克到 2300 毫克之间。
After one week, you might not physically feel the difference, but your body has already lowered its blood pressure.
一周后,你可能不会感觉到身体有什么变化,但你的血压已经降低了。
Your kidney is responsible for this by regulating what's inside your blood vessels.
When you're well hydrated and drinking fluids, it tells your body to excrete any extra water, and if you're dehydrated, it sends a signal to not only increase thirst, but to cause reabsorption of your fluids in the kidney, making your body hold onto more water.
This is all in an effort to keep the perfect balance of water and salt between your blood and cells.
But consuming lots of salt can sometimes get in the way of this process.
Since your body can't produce its own, we consume salt through the diet, where it's eventually absorbed into your blood.